TangleML Studio UI Guide
TangleML Studio provides a comprehensive web-based interface for building, managing, and running machine learning pipelines. This guide walks you through the three main areas of the application: Home screen, Editor, and Pipeline Run.
Home screen
The home screen serves as your dashboard for managing pipelines and monitoring runs across your TangleML instance.
All runs
The All Runs section displays a comprehensive list of all pipeline runs on your TangleML instance. This centralized view helps you track execution history and monitor pipeline performance across your organization.
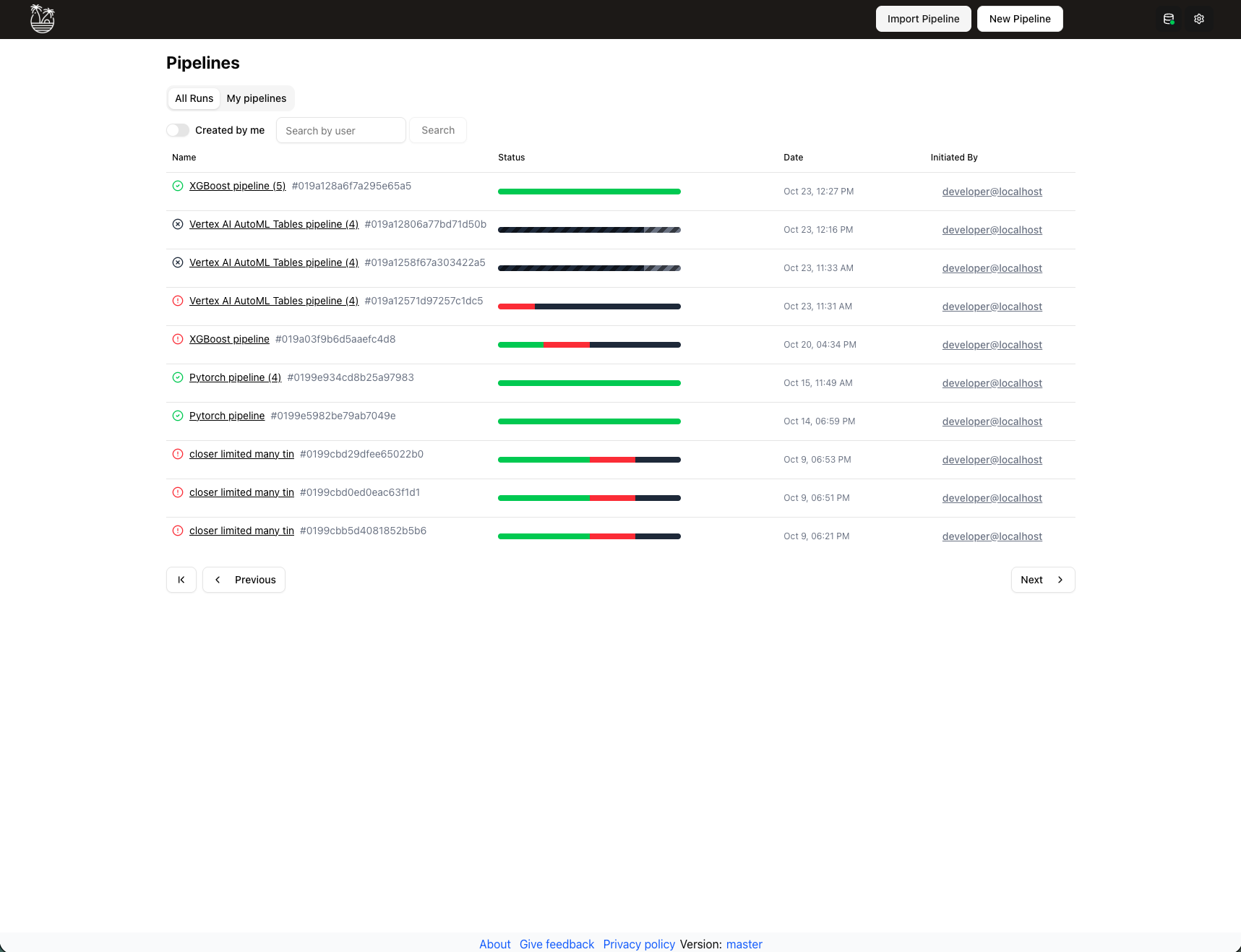
- Filtering: Filter runs by creator to find specific executions. Patila matches are not supported, you must use the full name.
- Run status: View the current status of each run (Running, Succeeded, Failed, Cancelled).
- Quick access: Click on any run to view detailed execution information.
My Pipelines
The My Pipelines section manages your draft pipelines stored locally in browser storage. This is your personal workspace for pipeline development before submission.
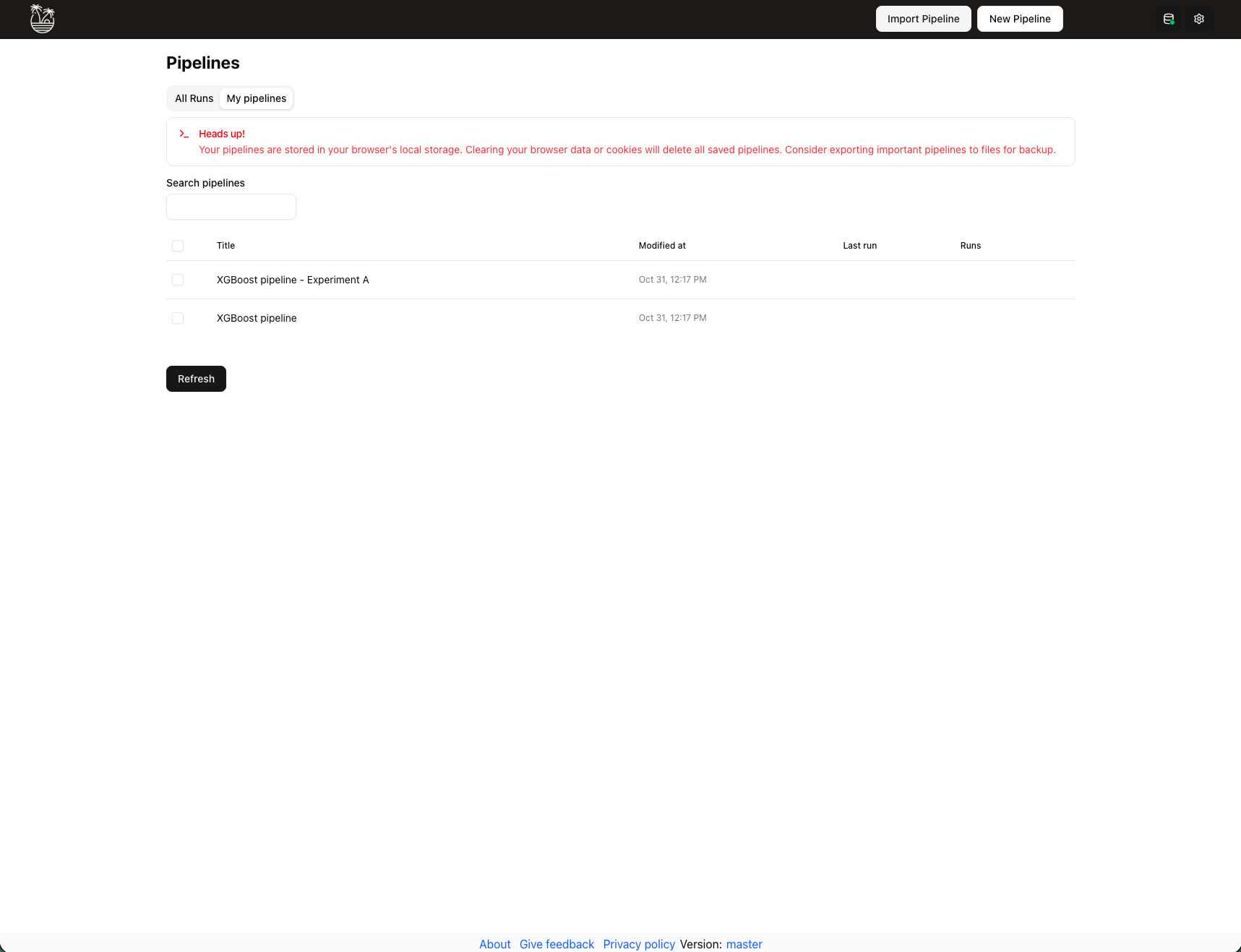
- Local storage: All draft pipelines are stored in your browser's local storage. For more on local vs shared storage, see Pipelines Peristence.
- Bulk operations: Select multiple pipelines using checkboxes for bulk delete operations.
- Run history: Pipelines with existing runs display a "runs" popover showing execution history.
- Quick actions: Edit, duplicate, or delete pipelines directly from the list.
Editor
The Editor is the heart of TangleML Studio, providing an intuitive drag-and-drop interface for building machine learning Pipelines.
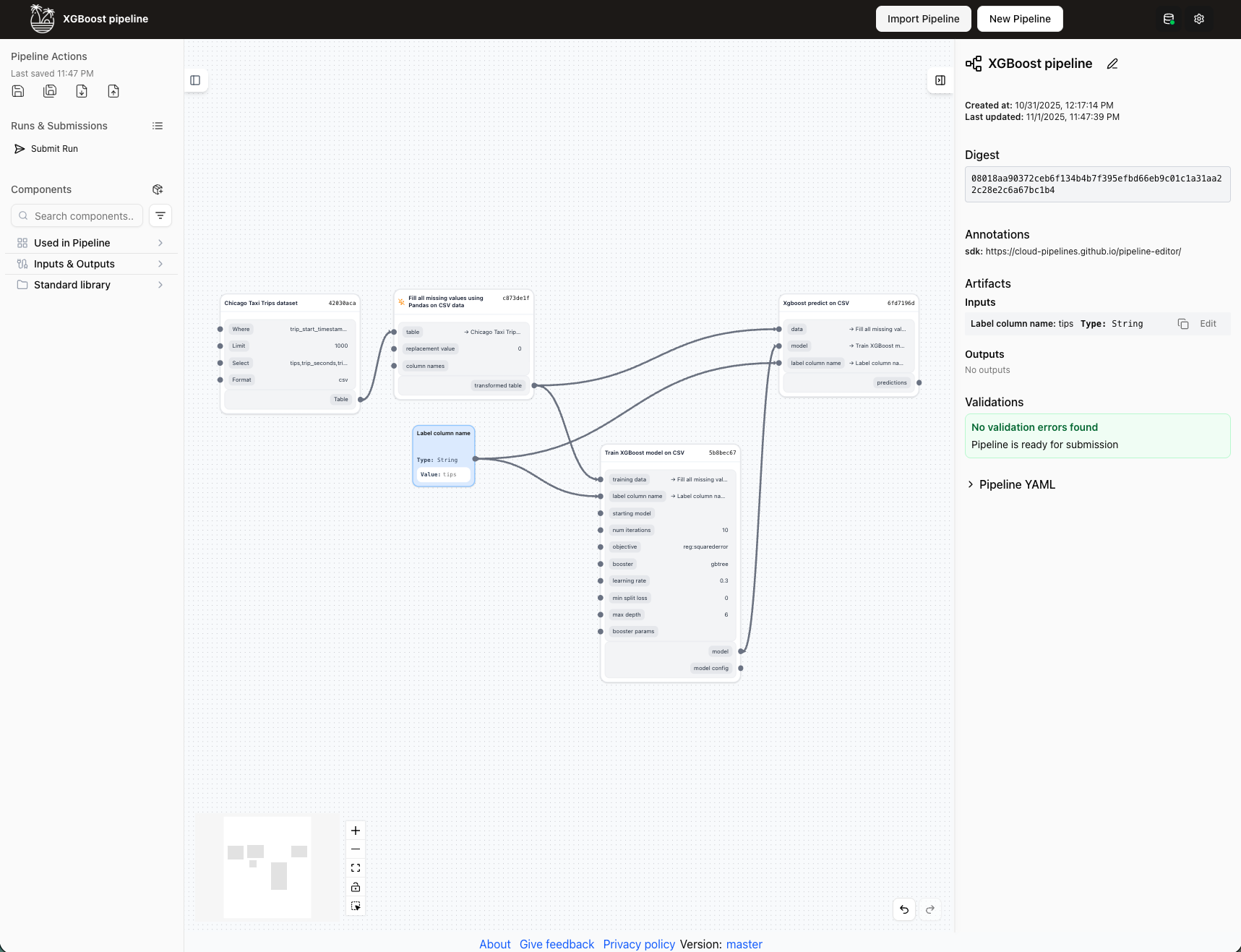
Layout overview
The Editor consists of four main areas:
- Top bar: Quick access to manage pipelines.
- Left Panel: Pipeline controls and component library.
- Canvas: Central workspace for visual pipeline construction.
- Right Panel: Context-sensitive information panel.
Top bar
The top bar provides quick access to essential functions:
- Pipeline name: Shows the current pipeline’s name. Click to edit and rename your pipeline.
- Import pipeline: Load a pipeline into the editor from a file or by pasting YAML content.
- New pipeline: Start a fresh, empty pipeline project.
- Backend status: Check the status of your backend connection at a glance.
- Settings: Access backend settings and adjust your personal preferences.
Left panel
The left panel organizes pipeline management and component access.
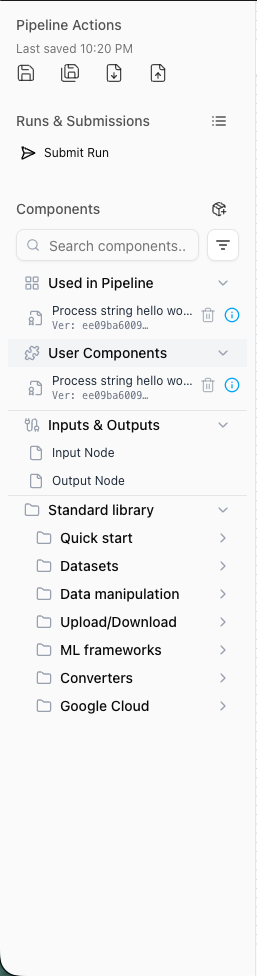
Pipeline actions
- Save Pipeline: Saves current state to browser local storage
- Save Pipeline As: Creates a copy with a new name
- Export Pipeline: Downloads pipeline as YAML file
- Import Pipeline: Load from file or paste YAML directly
Runs and submission
- Submit Run: Immediately schedules the current Pipeline for Execution
- Recent Pipeline Runs: Displays popover with recent runs for quick access
Components
Search functionality:
- Search by: Name, input name, input type, output name, or output type
- Toggle between partial match (default) and exact match
- Example: Search
CSVto find all CSV-related components
Component categories:
- Used in pipeline: Shows all components currently in your pipeline
- Click any component to navigate directly to it on the canvas
- User components: Your personal component library
- Components created or imported by you
- Stored locally in browser storage
- Special components: Input and output nodes for pipeline parameters
- Standard library: Hierarchical collection of standard components
- Data manipulation tools for various formats
- Machine learning frameworks (PyTorch, XGBoost, TensorFlow, TFX)
- Common operations and transformations
Each component has an info icon (ⓘ) that opens a detailed dialog with three tabs:
- Details: Complete component information
- Input/Output: Lists all inputs and outputs with metadata (required status, type, description)
- Implementation: Full YAML definition of the component
Canvas
The Canvas is your infinite workspace for visual Pipeline construction.
- Pan: Click and drag to move around the canvas
- Zoom: Scroll or use zoom controls to adjust view
- Mini-map: Bottom-left corner shows your current position in the pipeline
Canvas toolbar
The Canvas Toolbar provides a set of essential tools to manage and navigate your Pipeline workspace:

- Mini-map: Offers a visual overview of your entire pipeline layout, letting you quickly jump to different areas.
- Zoom In/Out: Adjusts the canvas scale so you can focus on details or see the bigger picture.
- Fit to View: Automatically rescales and centers your pipeline to fit the entire view.
- Lock: Prevents accidental movement of tasks, allowing you to navigate safely without disturbing your layout.
- Group Select: Enables you to select multiple tasks at once for bulk operations such as moving, deleting, or updating them.
Task representation
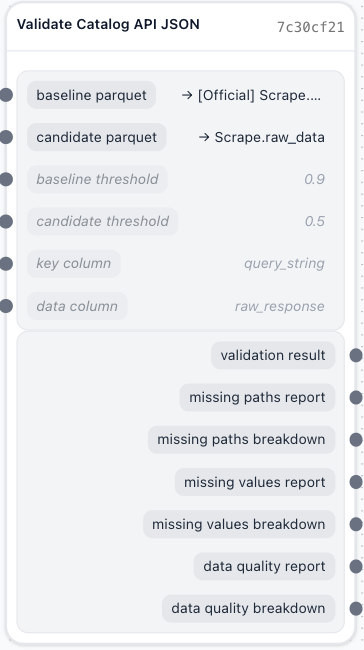
- Tasks appear as rectangles with inputs on the left, outputs on the right
- Connection points (handles) for creating data flows
- Visual indicators for validation status and recent changes. Red dot indicates a validation error.
Basic operations
- Add component: Drag from Component Library to Canvas
- Connect tasks: Click output handle and drag to input handle
- Move tasks: Click and drag to reposition
- Delete connection: Select connection and press Backspace
Undo/redo controls
The editor tracks the last 50 changes, and you can undo and redo changes from the bottom-right corner or using keyboard shortcuts. Changes are stored per session, and if you reload the page your history will be lost.
Group operations
To activate group operations, select Group Selection in the canvas toolbar. From there, you can:
- Delete: Remove all selected nodes and their connections.
- Duplicate: Create copies of selected nodes while preserving their connections.
- Update: Apply version updates or configuration changes to all selected nodes simultaneously. Useful when upgrading multiple components to newer versions.
- Move as group: Drag any selected node to move the entire selection while maintaining relative positions.
Use Ctrl/Cmd+A to select all nodes, then deselect specific ones with Ctrl/Cmd+Click.
Pipeline context panel
When no Task is selected, the panel shows pipeline-level information:
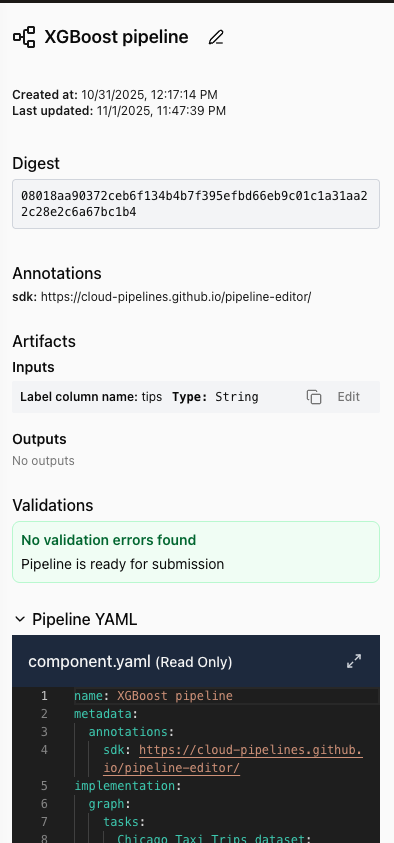
Pipeline information:
- Pipeline name with edit button
- Creation and last update timestamps
- Unique digest identifier (click to copy)
- Validation status and errors
Pipeline inputs/outputs:
- All pipeline parameters via Input/Output nodes
- Editable values for Input nodes (required)
- Copy values to clipboard
Pipeline YAML:
- View-only display of complete pipeline definition
- Full YAML content for reference
Arguments context panel
When a task is selected, the panel shows three tabs.
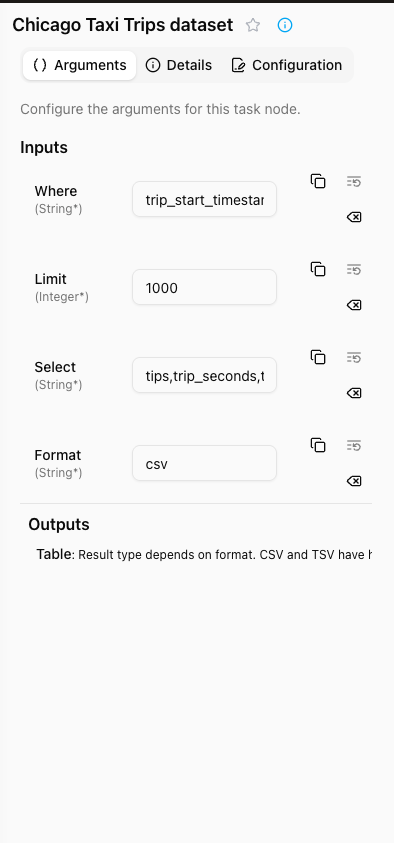
- Complete list of task inputs and outputs
- Required arguments marked with asterisk (*)
- Per-argument controls:
- Copy value to clipboard
- Reset to default value
- Exclude argument from execution
- Green indicator for recently changed values
- Expandable multi-line editor for complex values
- Click row to view argument description
When configuring component inputs, you have several actions available through the toolbar buttons:
| Action | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Copy value | Copies the current input value to clipboard | |
| Reset to default | Resets input to its default value from YAML | |
| Exclude argument | Excludes this input from execution | |
| Include argument | Re-includes a previously excluded input |
Exclude/include argument
When you use the Exclude Argument action, the input is removed from the execution parameters. This is especially helpful for optional inputs that you do not need. The input field will become dimmed, but you can still edit its contents if you wish.
Choosing the Include Argument action will re-add a previously excluded input. This returns the input to its active state in the pipeline. If the input was empty when you include it, it may automatically be filled in with the default value.
Empty input is not the same as excluded input. Excluded input is removed from the execution parameters, while empty input is still a value that will be passed to the task execution.
Understanding default values
Default values are specified in the component's YAML definition and serve as fallback values when an input is not explicitly provided. Authors specify default values in the component specification.
The default value shown in the UI comes from the component's YAML definition, but it may differ from what the actual component implementation uses.
Details Context Panel
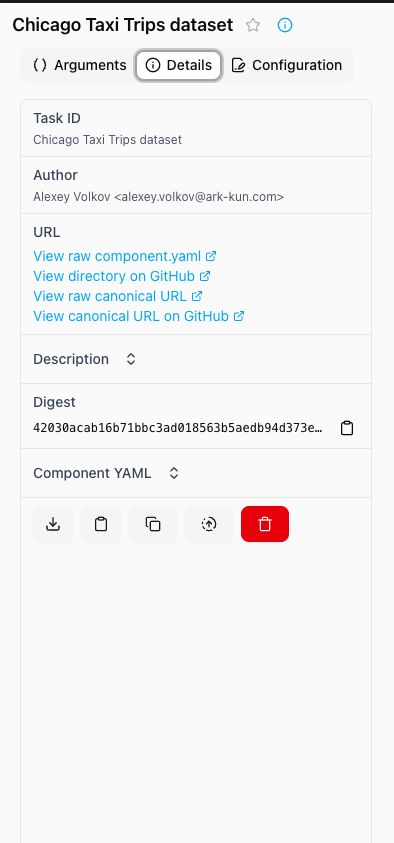
- Component information for selected Task
- Access to component YAML
- Action buttons:
- Download YAML
- Download Python code (if available)
- Copy YAML to clipboard
- Duplicate task
- Edit component definition (if enabled in preferences)
- Delete task
- Unique digest identifier
Configuration context panel
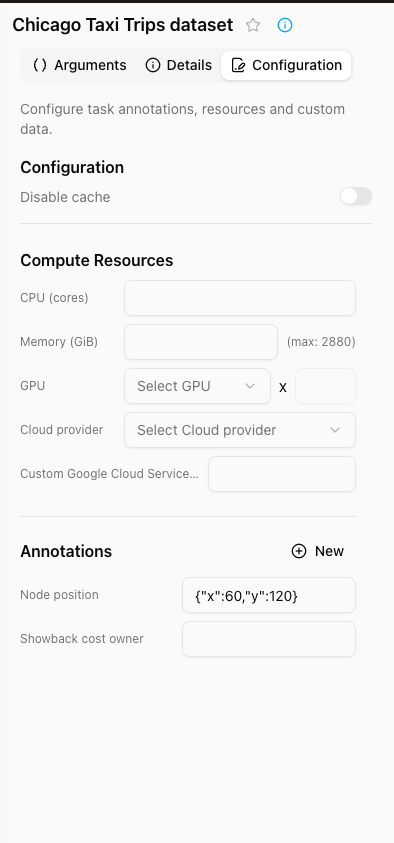
- You can disable cache for the Task.
- Configure compute resources:
- CPU cores
- Memory (GB)
- GPU enablement
- Cloud provider selection
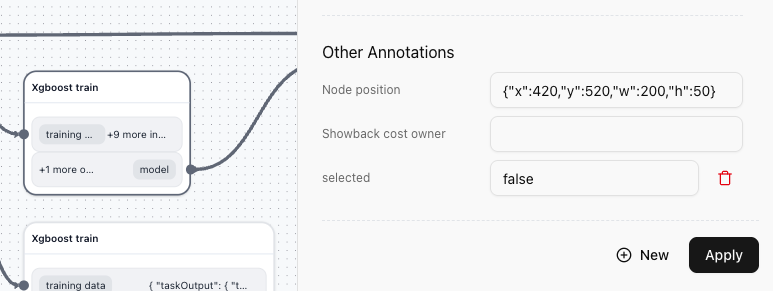
- Custom annotations section for additional metadata
You can collapse the task node. Just add a w and h field to your Node position annotation on a node.
Tasks with validation errors will prevent pipeline execution. Check the validation section to identify and resolve issues before submitting runs.
Pipeline Run view
The Pipeline Run view provides detailed insights into pipeline execution, allowing you to monitor progress, inspect outputs, and debug issues.
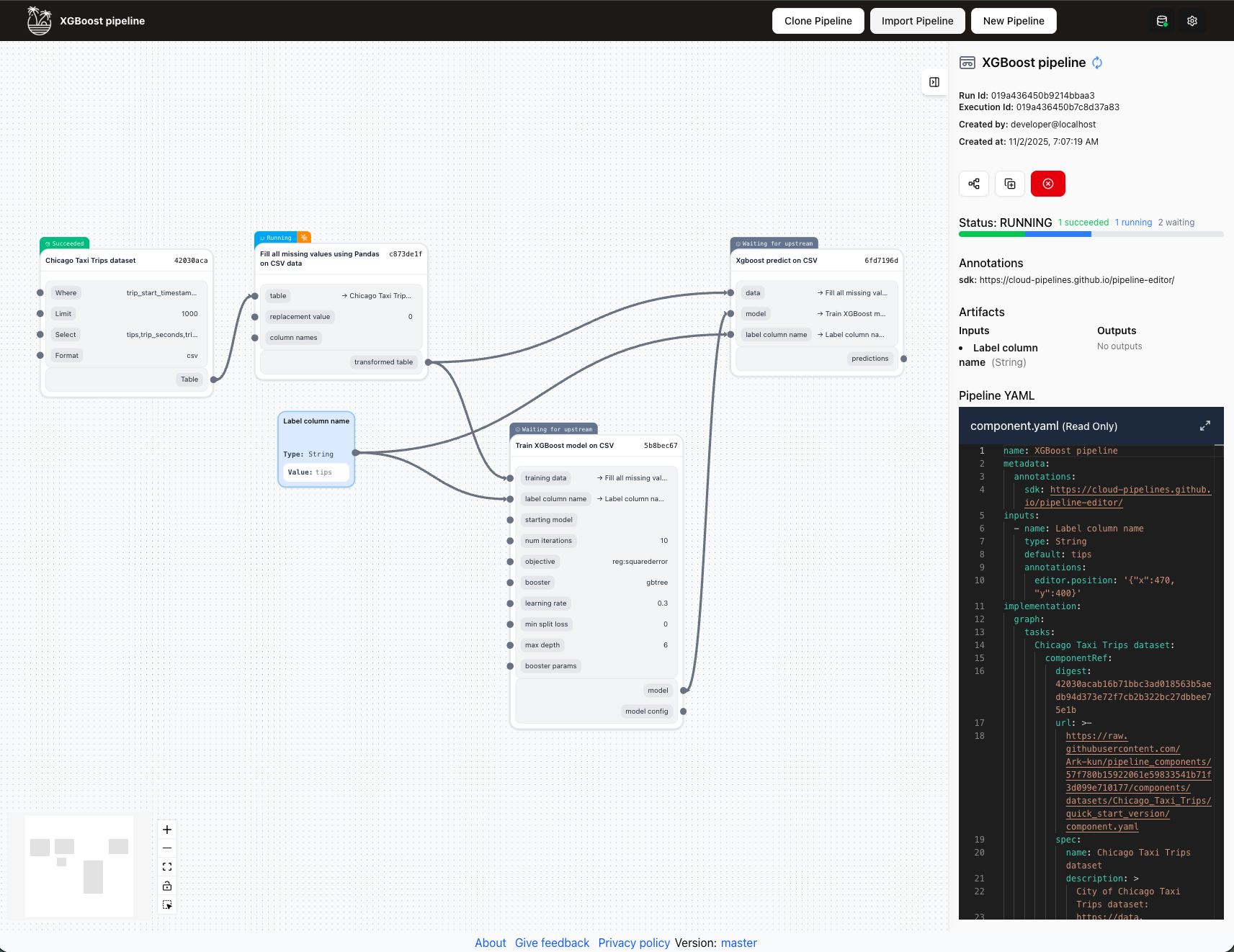
Run overview
The main area displays the pipeline graph with execution status for each task:
- Visual indicators show task status (Pending, Running, Succeeded, Failed, Skipped)
- Execution timeline and duration for completed tasks
- Real-time updates for running pipelines
Run actions
Available actions depend on run status:
- Inspect: Open the pipeline editor for the run. Only available for pipelines that are stored in the local browser storage.
- Cancel: Stop a running pipeline. Only user that created the run can cancel it.
- Re-run: Re-run a pipeline with same parameters.
- Clone: Create new pipeline from this run's configuration.
Use the logs tab to debug failed tasks. Error messages and stack traces help identify issues quickly.
Context panel
The right panel provides detailed information about the run or selected task.
Pipeline Run details (no task selected)
When viewing the overall run:
- Run status and metadata
- Start and end times
- Total duration
- Input parameters used
- Overall pipeline outputs
Task Execution details (task selected)
When a specific Task is selected, three tabs provide comprehensive Execution information:
1. Artifacts tab
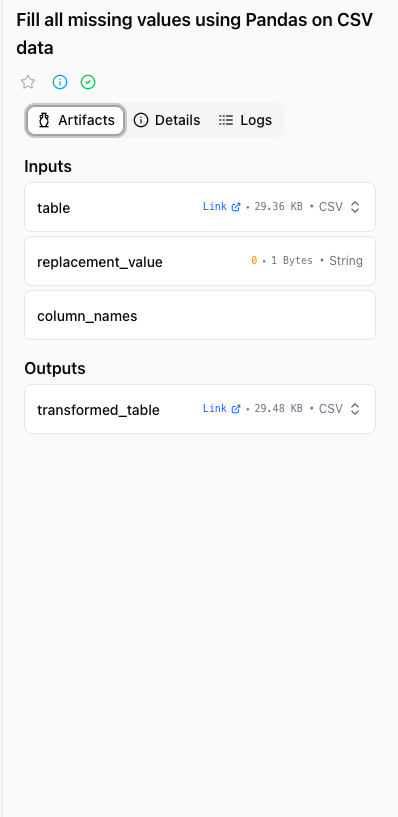
- Output artifacts produced by the Task
- Download links for files
- Preview for supported formats
- Artifact metadata (size, type, location)
2. Details tab
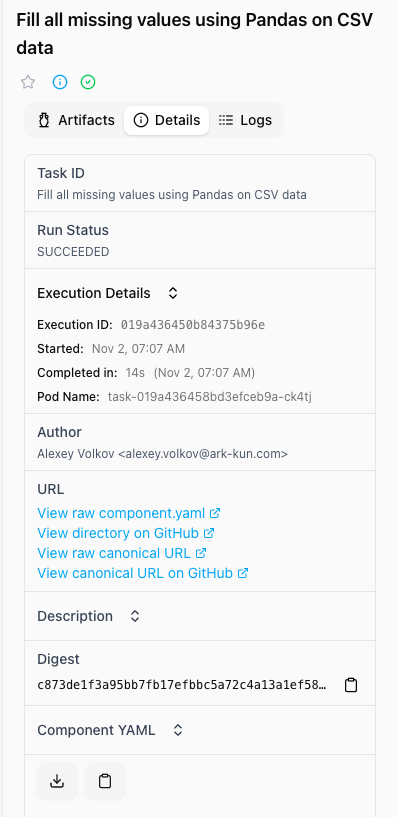
- Task Execution metadata
- Start and completion times
- Duration
- Resource usage statistics
- Component version used
- Execution environment details
3. Logs tab
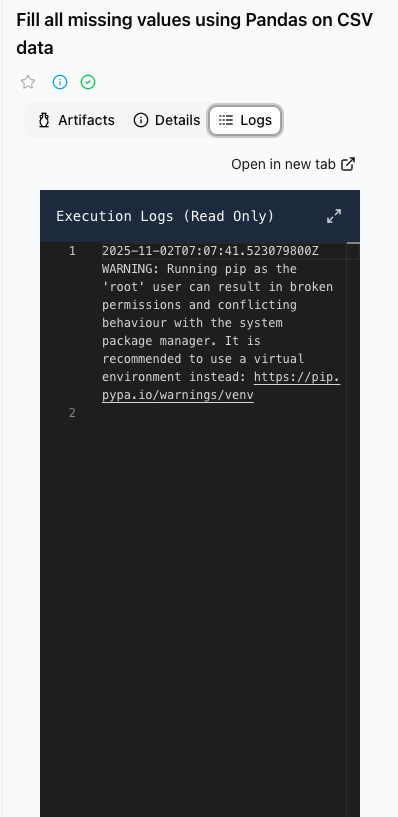
- Complete execution logs
- Stdout and stderr output
- System messages
- Error traces for debugging
- Log filtering and search capabilities
Best practices
- Save frequently: Use Save Pipeline regularly to preserve your work
- Validate before running: Check the validation panel for errors before submitting
- Use descriptions: Add meaningful descriptions to help others understand your pipeline
- Organize components: Keep your User Components library organized by removing unused items
- Monitor runs: Check the All Runs section to track pipeline performance over time
Keyboard shortcuts & hotkeys
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
Ctrl/Cmd + Z | Undo |
Ctrl/Cmd + Y | Redo |
Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + Z | Redo |
Delete/Backspace | Delete selected elements |
Shift + Delete/Backspace | Delete selected elements (skip confirmation) |
Shift + Drag | Full select multiple tasks (as a group) |
Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + Drag | Partial select multiple tasks (as a group) |
Ctrl/Cmd + Click | Select multiple tasks (individually) |
Ctrl/Cmd + A | Select all tasks |
Ctrl/Cmd + C | Copy selected tasks |
Ctrl/Cmd + V | Paste copied tasks |
Escape | Deselect all |
Troubleshooting
Common issues
Pipeline won't run:
- Check validation panel for errors
- Ensure all required inputs have values
- Verify component compatibility
Lost draft pipelines:
- Draft pipelines are stored in browser local storage
- Clearing browser data will remove drafts
- Always export important pipelines as YAML backups
Can't connect components:
- Verify input/output type compatibility
- Check for circular dependencies
- Ensure required inputs are satisfied
Remember that browser local storage has size limits. Export and backup important pipelines regularly to avoid data loss.